
In high-temperature industrial operations, the choice of refractory materials is crucial. Substandard refractory materials can lead to a series of problems, such as equipment damage, production interruptions, and increased maintenance costs. For example, if the refractory lining in a steel furnace fails due to poor performance, it can cause molten steel leakage, which is not only dangerous but also results in significant economic losses. This is where high-temperature magnesia-chrome bricks come into play.
High-temperature magnesia-chrome bricks are made from sintered magnesia and refractory-grade chromite ore as the main raw materials, bonded with silicates. Sintered magnesia has high purity and excellent refractoriness, which provides the basic high-temperature resistance of the bricks. Refractory-grade chromite ore enhances the corrosion resistance and thermal shock resistance of the bricks. The combination of these two materials endows magnesia-chrome bricks with outstanding overall performance.

The manufacturing process of high-temperature magnesia-chrome bricks involves precise batching, mixing, molding, and high-temperature firing. This process ensures the uniform distribution of raw materials and the formation of a dense structure, which significantly improves the strength and durability of the bricks. Compared with some traditional refractory materials, the production process of magnesia-chrome bricks is more advanced, resulting in better performance and longer service life.
High-temperature magnesia-chrome bricks have remarkable performance. Their refractoriness exceeds 2000°C, and the load-softening temperature is above 1550°C. They can maintain stable volume at high temperatures, which is crucial for maintaining the structural integrity of high-temperature equipment. In terms of corrosion resistance, they can effectively resist the erosion of various slag and molten metals.
Let's compare the performance of magnesia-chrome bricks with magnesia bricks in a thermal cycling environment. The following table shows the comparison results:
| Brick Type | Refractoriness (°C) | Load-softening Temperature (°C) | Thermal Cycling Resistance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Magnesia-chrome Bricks | >2000 | >1550 | Excellent |
| Magnesia Bricks | 1800 - 1900 | 1450 - 1500 | Good |
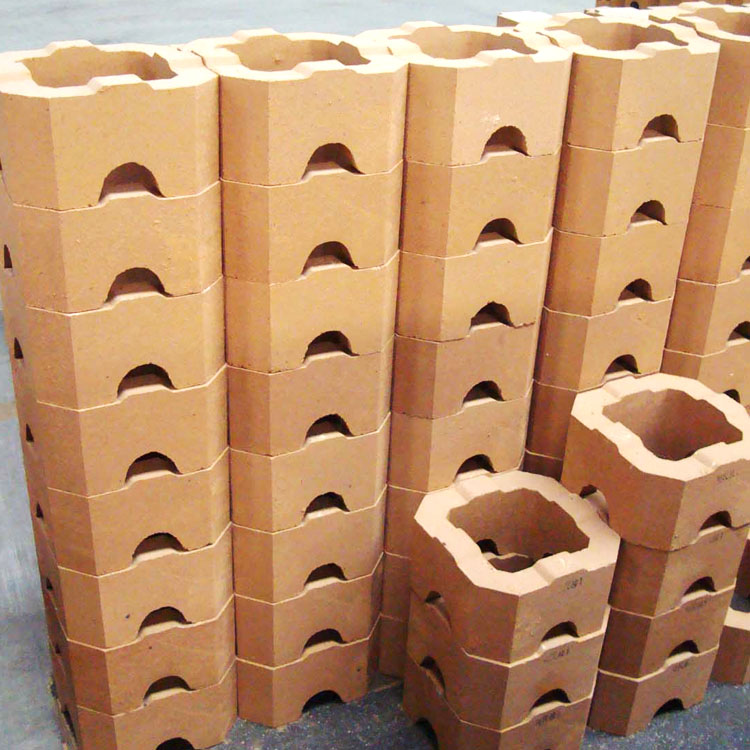
High-temperature magnesia-chrome bricks have been widely used in various high-temperature industries. In the steelmaking industry, they are used in the lining of converters, electric arc furnaces, and ladles, effectively improving the service life of the furnaces and reducing production costs. In the glass manufacturing industry, magnesia-chrome bricks are used in the melting furnaces, providing stable high-temperature performance and ensuring the quality of glass products.
.jpg)
In conclusion, high-temperature magnesia-chrome bricks are an ideal choice for high-temperature applications. With their high strength, excellent corrosion resistance, and superior thermal cycling performance, they can meet the strict requirements of various high-temperature industries. If you are still considering which refractory materials to choose for your high-temperature equipment, we encourage you to contact us for more information or request a free sample.
Ready to enhance your high-temperature operations? Contact us now at [email protected] or visit our website www.example.com to learn more and place an order!

